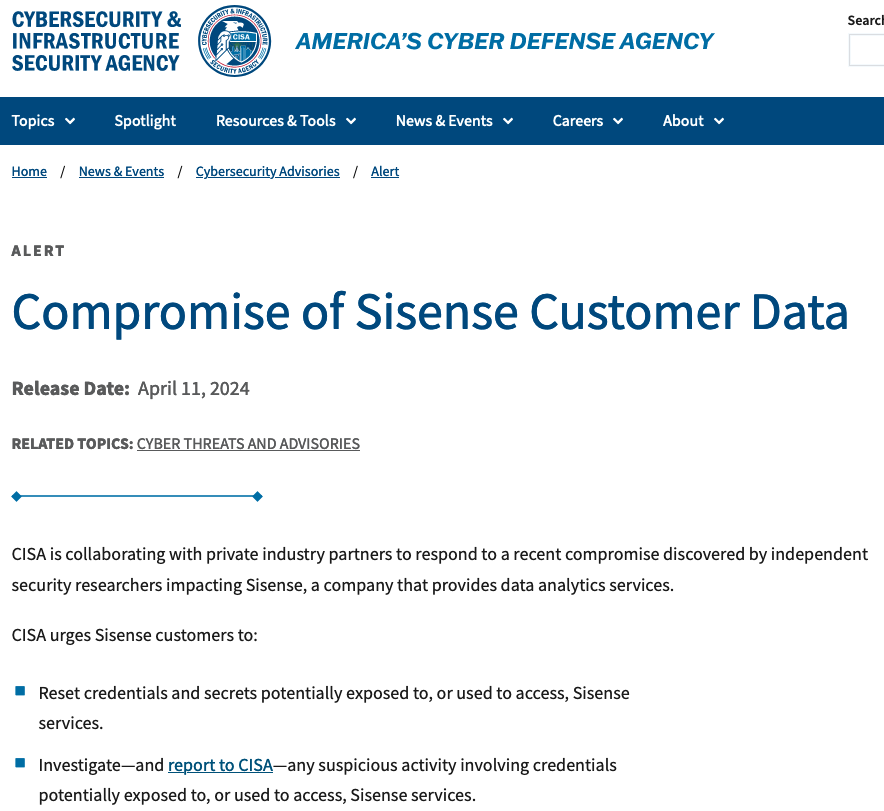
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) said today it is investigating a breach at business intelligence company Sisense, whose products are designed to allow companies to view the status of multiple third-party online services in a single dashboard. CISA urged all Sisense customers to reset any credentials and secrets that may have been shared with the company, which is the same advice Sisense gave to its customers Wednesday evening.
New York City based Sisense has more than 1,000 customers across a range of industry verticals, including financial services, telecommunications, healthcare and higher education. On April 10, Sisense Chief Information Security Officer Sangram Dash told customers the company had been made aware of reports that “certain Sisense company information may have been made available on what we have been advised is a restricted access server (not generally available on the internet.)”
“We are taking this matter seriously and promptly commenced an investigation,” Dash continued. “We engaged industry-leading experts to assist us with the investigation. This matter has not resulted in an interruption to our business operations. Out of an abundance of caution, and while we continue to investigate, we urge you to promptly rotate any credentials that you use within your Sisense application.”
In its alert, CISA said it was working with private industry partners to respond to a recent compromise discovered by independent security researchers involving Sisense.
“CISA is taking an active role in collaborating with private industry partners to respond to this incident, especially as it relates to impacted critical infrastructure sector organizations,” the sparse alert reads. “We will provide updates as more information becomes available.”
Sisense declined to comment when asked about the veracity of information shared by two trusted sources with close knowledge of the breach investigation. Those sources said the breach appears to have started when the attackers somehow gained access to the company’s code repository at Gitlab, and that in that repository was a token or credential that gave the bad guys access to Sisense’s Amazon S3 buckets in the cloud.
Both sources said the attackers used the S3 access to copy and exfiltrate several terabytes worth of Sisent customer data, which apparently included millions of access tokens, email account passwords, and even SSL certificates.
The incident raises questions about whether Sisense was doing enough to protect sensitive data entrusted to it by customers, such as whether the massive volume of stolen customer data was ever encrypted while at rest in these Amazon cloud servers.
It is clear, however, that unknown attackers now have all of the credentials that Sisense customers used in their dashboards.
The breach also makes clear that Sisense is somewhat limited in the clean-up actions that it can take on behalf of customers, because access tokens are essentially text files on your computer that allow you to stay logged in for extended periods of time — sometimes indefinitely. And depending on which service we’re talking about, it may be possible for attackers to re-use those access tokens to authenticate as the victim without ever having to present valid credentials.
Beyond that, it is largely up to Sisense customers to decide if and when they change passwords to the various third-party services that they’ve previously entrusted to Sisense.
Earlier today, a public relations firm working with Sisense reached out to learn if KrebsOnSecurity planned to publish any further updates on their breach (KrebsOnSecurity posted a screenshot of the CISO’s customer email to both LinkedIn and Mastodon on Wednesday evening). The PR rep said Sisense wanted to make sure they had an opportunity to comment before the story ran.
But when confronted with the details shared by my sources, Sisense apparently changed its mind.
“After consulting with Sisense, they have told me that they don’t wish to respond,” the PR rep said in an emailed reply.
Nicholas Weaver, a researcher at University of California, Berkeley’s International Computer Science Institute (ICSI) and lecturer at UC Davis, said a company entrusted with so many sensitive logins should absolutely be encrypting that information.
“If they are hosting customer data on a third-party system like Amazon, it better damn well be encrypted,” Weaver said. “If they are telling people to rest credentials, that means it was not encrypted. So mistake number one is leaving Amazon credentials in your Git archive. Mistake number two is using S3 without using encryption on top of it. The former is bad but forgivable, but the latter given their business is unforgivable.”

